Last week, when most mainstream media was in the middle of yet another paroxysmal bout of Islamophobia over a thirteen-year-old child’s wish to wear the hijab to school, I was thinking: why is hijabophobia the most acceptable manifestation of the hatred of Islam in Kerala? Why is it that it seems to provoke many non-Muslim women to the point of anti-Muslim hysteria?
Continue reading Rotting Civil Society, Mounting Insecurity: Understanding Hijabophobia in KeralaCategory Archives: Debates
Postcolonial Theory and the “Decolonization of the Indian Mind” : Professor Meera Nanda

Indian Diaspora Washington DC lecture series
Topic: Postcolonial Theory and the “Decolonization of the Indian Mind”
Speaker: Professor Meera Nanda
Finally, an Answer to Why Kerala’s CPM-led Government is Determined to Break the ASHA Workers’ Strike
Finally, I am able to understand why the government of Kerala, led by a leading communist party, the CPM, is so doggedly against the demands of Kerala’s internationally-celebrated ground-level women health workers — the ASHA workers — who have been on strike since February 2025.
Continue reading Finally, an Answer to Why Kerala’s CPM-led Government is Determined to Break the ASHA Workers’ StrikeColonialism, Modernity and Science: K. Sridhar
[This post is the seventh essay of the series in Kafila titled Decolonial Imaginations. Links to the previous essays are given at the end.
The terms ‘decolonization’ or ‘decolonial’ have become quite critical now, given that the impulse of justice lies at the core of these concepts. Neither postcolonial nor decolonial perspectives are compatible with right-wing ideologies but the fact that Hindutva ideologues in India and the rightwing globally are now trying to appropriate that language makes it seem to some that the very idea of the postcolonial or decolonial is suspect. We believe that this demonizing of decolonial theory from a position defensive of the European Enlightenment needs to be unpacked in the interests of a mutually productive debate. Kafila will be publishing a series of interventions on what the idea of the decolonial imagination involves, locating decolonial theory as speaking from the margins, drawing attention to identities which the orthodox Left subsumed under ‘class’ and which the rightwing in India seeks to assimilate into Brahminism. Additionally the orthodox left’s rejection of spiritual beliefs and inability to engage with them is also a factor that may have produced the space for right wing appropriations of a field marked “religion”.
We hope that these interventions will clear the ground for productive conversations on the left rather than polarised and accusatory claims.]
It is impossible to think of modernity and colonialism, without thinking of their third sibling – science. They are not just siblings, in fact, but a set of triplets which took birth within the same western context and period – and hence, the adjectives ‘modern’ and ‘western’ are used to qualify science, often by the colonizers themselves. Just as the notion of ‘savage native’ was a part of colonial construction, so was the idea of ‘modern science’. Not only did the colonial powers conquer people and knowledge systems across the world, but they also established hegemony within their own societies, colonizing them from within. This was done using complex mechanisms of power, control and appropriation. Continue reading Colonialism, Modernity and Science: K. Sridhar
Javed Akhtar, Bollywood and Urdu’s Ghostly Existence – Rashid Ali
Guest post by RASHID ALI

Javed Akhtar’s recent ‘exile’ from the West Bengal Urdu Academy event did more than generate headlines. It dwarfed a bigger debate about Urdu in Hindi cinema, which was the event’s main theme. The media precipitately reduced the whole issue to the conflict between the lyricist and the Urdu Academy. The controversy carried a tinge of ‘Muslim fundamentalism,’ reflecting today’s cultural and political ideologemes. However, the discussion on Bollywood’s uneven relationship with Urdu was lost in the sound and fury of cultural climate of the country. Et tu, Brutus?’ finds a new stage – ‘Et tu, Bollywood?’ You speak against the very world that gives you voice. Continue reading Javed Akhtar, Bollywood and Urdu’s Ghostly Existence – Rashid Ali
Red Dreams, Saffron Marches – Longue Durée of India’s Struggles and Strategies of Power: S. M. Faizan Ahmed
Guest post by S.M. FAIZAN AHMED
[The author writes about the current scenario, reflecting on the one hundred years of the communist movement as well as of the RSS. In these important reflections Ahmed recounts the great achievements of the communist Left, while at the same time speculating on where the RSS scored over it – leaving us with a number of questions to seriously ponder about. – AN]

On October 1, 2025, a day before Gandhi’s birth anniversary, long revered and associated with ahimsa and moral conscience, the government unveiled a ₹100 coin at the Dr. Ambedkar International Centre, 15 Janpath, marking a century of the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh. A day earlier, as if to turn ideology into spectacle, a Shakha parade, named Path Sanchalan, traced its way through Jawaharlal Nehru University—once a fortress of dissent and the audacious poetry of thought. The rhythmic march of uniformed bodies through corridors once alive with debate did more than display ceremony; it signaled a shift in the republic’s moral conscience, where the choreography of discipline seeks to mute the dialectic of doubt, and the university—once a sanctuary of questioning minds—becomes a stage for the theatre of obedience. Continue reading Red Dreams, Saffron Marches – Longue Durée of India’s Struggles and Strategies of Power: S. M. Faizan Ahmed
Decolonizing the ‘Colonial-Brahmanical’ – Thinking outside Modernity: Sunandan K N
[This post is the sixth essay of the series in Kafila titled Decolonial Imaginations. Links to the previous essays are given at the end.
The terms ‘decolonization’ or ‘decolonial’ have become quite critical now, given that the impulse of justice lies at the core of these concepts. Neither postcolonial nor decolonial perspectives are compatible with right-wing ideologies but the fact that Hindutva ideologues in India and the rightwing globally are now trying to appropriate that language makes it seem to some that the very idea of the postcolonial or decolonial is suspect. We believe that this demonizing of decolonial theory from a position defensive of the European Enlightenment needs to be unpacked in the interests of a mutually productive debate. Kafila will be publishing a series of interventions on what the idea of the decolonial imagination involves, locating decolonial theory as speaking from the margins, drawing attention to identities which the orthodox Left subsumed under ‘class’ and which the rightwing in India seeks to assimilate into Brahminism. Additionally the orthodox left’s rejection of spiritual beliefs and inability to engage with them is also a factor that may have produced the space for right wing appropriations of a field marked “religion”.
We hope that these interventions will clear the ground for productive conversations on the left rather than polarised and accusatory claims.]
This short essay builds on the articles published in this series and has already explored the various ways in which the concept of de-colonization is articulated, appropriated and adapted in various historical contexts in India and elsewhere. This note aims to map, in a preliminary fashion, the divergent engagements with questions concerning caste across three key groups – colonialists, nationalists (including the Hindutva nationalists), and postcolonial and decolonial practitioners in the last two centuries. This note does not purport to break new empirical ground but instead assembles and juxtaposes existing academic and public arguments to construct a focused framework for comparison.
It is important to begin with the now established argument that concepts are not static but dynamic entities, formed, transformed and deployed along historical processes. In larger Humanities and Social Science disciplines, historians, philosophers, anthropologists and linguists have increasingly shifted the question from ‘what does a concept or a category or just a noun mean’ to ‘what does it do’. This shift posits that meaning is not a stable core but a secondary effect created from practice through a process of ‘densification’. We can observe this in Foucault’s inquiries into the concept of madness or Wittgenstein’s exploration of the performative nature of language. While the dominant forces have the power to deploy a category more widely and to limit its interpretations or in other words have the power to solidify and concretize the uses and effects of the category, they cannot guarantee to reduce this category to a singular use/meaning or limit its interpretation. Hence the importance of the analysis of the travel and transformation of categories in various routes, its adaptations and mutations across various historical contexts and times.
Colonialism held divergent meanings and ‘affected’ differently for different groups of colonised, who in turn responded differently in varied temporal and spatial contexts. In what follows, I will briefly describe how colonialism affected the discourse and practice of caste and how different sections of the colonised reciprocated and acted on these colonial interventions. By doing so, I will demonstrate that, while colonialists, upper caste and Hindutva nationalists, and Leftists at some or other point have taken ostensibly anti-caste positions, their intentions or outcomes were not similar and all of them varied drastically from the radical project of annihilation of caste proposed by Ambedkar.
A parallel divergence exists within academic scholarship, where the analysis of caste from nationalist, postcolonial and decolonial perspective have criticized caste system but from different standpoints and with different objectives. It will therefore be both analytically trivial and politically dangerous to equate Ambedkar’s radical anti-caste position with Hindutva rhetoric against caste. Similarly equating a genuine decolonial position on caste with Hindutva’s strategic engagement with caste or about any other issues, can only stem from either a misreading or a cynical anxiety of losing one’s own relevance.
Colonial practice was never governed by a single monolithic principle; instead it was characterised by contradictions, ironies and exceptions that became the very norm of colonial rule. A pivotal moment in this history was the orientalist introduction of ‘Hindu’ as a unified religious category which fundamentally reshaped the colonial discourse on caste in India. Earlier, the category jathi dominated in the organisation of social practices and in the reflection of these practices. This does not mean jathi remained static in the precolonial period. As a dynamic system jathi underwent many transformations but remained hierarchical all through this period. The orientalists understood jathi as the essential principle of Hindu religion but also created a historical myth in which there existed a Hindu golden past which was destroyed by the Islamic invasions. This enabled many problematic concepts such as the idea that Hindu religion existed from the Vedic period onwards, and that all precolonial kingdoms were religious or something articulated as Sanathana Dharmam was part of this Hindu religion.
These notions are dominant even in contemporary debates and in common sense. The Hindutva history is completely premised on this colonial historical myth (not on the postcolonial or decolonial critique of these concepts) which the Hindutva propagandist will never admit. While they wholeheartedly embrace this part of colonial history, they vehemently oppose the theory of ‘Brahmanical despotism’ which was also an integral part of the colonial understanding of the Hindu religion. In the so called ‘decolonisation project’ of the Hindutva only the latter part is to be decolonised. To be exact, even the other versions of nationalist history in the first half of the twentieth century – Gandhian, Ambedkarite, Nehruvian, Marxist – incorporated some or other elements of this colonialist orientalist interpretation. Decolonisation project attempts to point out not only the overlaps of the nationalist project with colonial one, but also focuses on how this enables the current forms of domination and subordination.
Postcolonial and decolonial histories challenged both colonial interpretation of caste and its nationalist adaptations as well. Nicholas Dirks explained how caste identities were re-constructed and even rigidified through various colonial governing practices. This was often misinterpreted as though he was arguing that caste was a pure colonial construction, which is clearly a Hindutva argument which, unlike Dirks, completely overlooks the inhuman caste domination and violence in the precolonial period. G Aloysius in his book Nationalism without a Nation analysed how caste was central to the nationalist political position of anti-colonialism. Lata Mani’s work on Sati (Contentious Traditions: The Debate on Sati in Colonial India) shows how colonialist and the upper castes together reconstructed ‘traditions’ which also became the basis for the reform narrative which attempted to separate good traditional practices from superstitions.
The idea that jathi was an exception that accidently emerged in the long history of Hindu religion was central to Hindu reform attempts and this was the exact point that Ambedkar rejected in his essay ‘Annihilation of Caste’. While this essay premises existence of Hindu religion based on Shasthras (Orthodoxy), which one can now see as an orientalist construction, his arguments were anchored against the colonial and nationalist narratives of a Hindu golden past and against the possibility of an egalitarian reformed Hinduism as depicted by Hindu reformers of the period. The fact that the Hindutva propagandists attempt to make him one of the many Hindu reformers does not make him a ‘strange bedfellow’ or ‘enabler’ of Hindutva politics. On the contrary, his political philosophy has become the inspiration for anti-Hindutva politics in the twenty-first century.
Ambedkar’s critique focused on the social practices and political ideology of casteism embedded in Hindutva politics. Decolonial historians have extended this critique by analysing the role of caste not just in traditions but also in what is described as modern as well. This scholarship is inspired by feminist standpoint theories and black and queer feminist (many among them are scientists) critique of Science (Sandra Harding, Karen Barad, Chanda Prescod-Weinstein etc.), critique of modern forms of knowledge production from indigenous perspective (Linda Tuhiwai Smith, Dian Million, Candis Callison) and Indigenous critique of modernity and its genocidal developmental practices in India (Abhay Xaxa, Hansda Sowvendra Shekhar, Jacinta Kerketta) and so on. In a close reading of these works one could easily recognize that they are all part of a politics that challenges racist, casteist, patriarchal dominations and other right wing ideologies.
Ajantha Subramanian in her book Caste of Merit: Engineering Education in India shows how brahmanical notions of merit were embedded from the very beginning of IITs in India. Her analysis shows that the upper caste dominance in the so-called Nehruvian temples of modernity is not an exception but by design. The history of IIT Roorkee will also tell a similar story. Started as Thomason College of Civil Engineering in 1847 to train Indians as engineers for the Ganga Canal Project, the engineering education here was based on the workshop model as it was in Europe and other places. However as most of the students in the first three batches were upper caste Bengalis, the learning based on doing was not successful. After an inquiry committee report it was decided that there should be a three tier system in which the top tier will be a fully theoretical (mental labour based) education in the classroom, the middle level will be half classroom and half workshop based and the lowest level will be fully in the workshop. This is the model that was replicated in technical education as the three tier system of Engineering College, Polytechnic, and ITIs. Here caste hierarchy was clearly mapped into the hierarchy of knowledge in which mental labour is separate from the manual labour and superior to the latter. This separation of theory from practice (mental labour from manual labour) is central to all forms of modern knowledge practices not only in India but everywhere in the world. Hence wherever these institutions emerged in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, they incorporated the local power hierarchies into their notion of knowledge. Considering this history, it is not an accident that the Science and Technology institutions and science and technology departments in Universities are the worst domains of caste discrimination and exclusion. This is not to say that Social Science as a discipline or the departments are egalitarian. It is the same modernist and casteist notion that established the divide between theoretical Brahmins and empirical Shudras, a Gopal Guru has already pointed out.
In my book Caste, Knowledge and Power: Ways of Knowing in the Twentieth Century Malabar, I have demonstrated that caste discrimination in the domain of knowledge production in India is not just institutional but epistemological as well. Hence, I have argued that the dominant form of modernity in India in general and its forms of knowledge production in particular need to be understood not as Western, Scientific, Eurocentric or Universal but as Colonial-Brahmanical. Brahmanical understanding of jathi and gender are part of the epistemology and practices of all modern institutions. In other words, any attempt of decolonisation will be anti-colonial as well as anti-Brahmanical and will inherently be an anti-Hindutva project as well.
In conclusion, It is critical to recognise that the Hindutva appropriation of icons like Gandhi or Ambedkar, their attack on Nehru or their revivalist understanding of Science and Technology, should not circumscribe one’s own critique of Gandhi or Nehru or Science or be apologetic in fear of appropriation. An appropriate response would not be that ‘we are not abandoning rationality’ or ‘we are not relativists’ or ‘we believe in different kinds of Science’. Rather, we must reject the foundational role of the very binaries of – Rational/ irrational, absolute / relative, modernity / tradition – to advance a politics of equality and fraternity. The more productive analytical framework would be to ask what these concepts do: Do they enable and intertwine with other actions for a more democratic and equal world or do they reinforce social hierarchy?
Sunandan KN is Associate Professor, Azim Premji University, Bangalore. The opinions are personal.
Sleeping with the enemy? Postcolonialism, misread and misjudged: Shamayita Sen
Beyond philosophical gaslighting – seven theses on decolonization/ decoloniality: Aditya Nigam
Anti-colonial thought and the global right – an untenable alliance: Ishan Fouzdar
The Struggle for a ‘Coloured Modernity’: Meghna Chandra and Archishman Raju
Books as Crime ? – Whether J and K High-court Will End the ’Unprecedented Situation’ ?
‘So you are the little woman who wrote the book that made this great (American) civil war’
— Abraham Lincoln to Harriet Beecher Stowe, author of Uncle Tom’s Cabin
The Writers’ Police !
Bruno Fulgini, a nondescript employee at the French Parliament, would not have imagined in his wildest dreams that his tedious and boring job at the Parliament library would lead him to a treasure hunt of another kind.
Nearly two decades back one witnessed him metamorphose into an author and editor, thanks to the sudden discovery of old files of the Paris police, which provided details of its surveillance work done way back in 18 th century. A report filed by AFP then, quotes Fulgini tell us that ’Beyond criminals and political figures, there are files on writers and artists. In some cases, they go far in their indiscretions.’….
It was clear to these protectors of internal security of a tottering regime that the renowned literati then viz. Victor Hugo, Balzac or Charles Dickens, might be writing fiction, but their sharp focus on the hypocrisy of the aristocrats or the livelihood issues of ordinary people is adding to the growing turmoil in the country. They knew very well that they might be writing fiction for the masses but it is turning out to be a sharp political edge that hit the right target and is becoming a catalyst for change.
The Parisian police was engaged in tracking down the daily movements of the writers, was more subtle in its actions; its present-day counterparts in the West do not seem to have such patience.
The strongest democracy in the world namely the US has of late become a site of an ’unprecedented’ ’Multi-level barrage of US book bans’ as per PEN America [1]….
And now there are indications that the biggest democracy in the World namely India is keen to follow the footsteps of the strongest democracy ?
Or it is too early to say that .[ Read the full article here : http://mainstreamweekly.net/article16227.html
Protest Assault on Adivasi Youth Leader Rama Kankonkar, Lawless Casino-based Development in Goa: NAPM
Statement by NATIONAL ALLIANCE OF PEOPLE’S MOVEMENTS demands principled investigation to establish command responsibility. It also demands that Govt review the unsustainable and unjust ‘development’ model fuelled by land mafias and casino interests in Goa .
National Alliance of People’s Movements (NAPM) unequivocally condemns the heinous assault on adivasi youth leader, Rama Kankonkar on 18th September, the subsequent intimidation against another activist Swapnesh Sherlekar, and the alarming descent into lawlessness that these incidents in Goa exemplify. We extend unwavering solidarity to Rama Kankonkar, Swapnesh Sherlekar and the people of Goa who continue to fight for justice, environmental protection, and the preservation of their collective identity. We also demand adequate protection to these activists, principled investigation to establish command responsibility and a review of the current unsustainable, unjust and unsafe ‘development’ model; fuelled by land mafias and casino interests. Continue reading Protest Assault on Adivasi Youth Leader Rama Kankonkar, Lawless Casino-based Development in Goa: NAPM
The Struggle for a ‘Coloured Modernity’: Meghna Chandra and Archishman Raju
[This post is the fifth essay of the series in Kafila titled Decolonial Imaginations. Links to the previous essays are given at the end.
The terms ‘decolonization’ or ‘decolonial’ have become quite critical now, given that the impulse of justice lies at the core of these concepts. Neither postcolonial nor decolonial perspectives are compatible with right-wing ideologies but the fact that Hindutva ideologues in India and the rightwing globally are now trying to appropriate that language makes it seem to some that the very idea of the postcolonial or decolonial is suspect. We believe that this demonizing of decolonial theory from a position defensive of the European Enlightenment needs to be unpacked in the interests of a mutually productive debate. Kafila will be publishing a series of interventions on what the idea of the decolonial imagination involves, locating decolonial theory as speaking from the margins, drawing attention to identities which the orthodox Left subsumed under ‘class’ and which the rightwing in India seeks to assimilate into Brahminism. Additionally the orthodox left’s rejection of spiritual beliefs and inability to engage with them is also a factor that may have produced the space for right wing appropriations of a field marked “religion”.
We hope that these interventions will clear the ground for productive conversations on the left rather than polarised and accusatory claims.]
The excerpt published in The Wire of Meera Nanda’s “Decolonising Ourselves into a Hindu Rashtra” argues that postcolonial and decolonial theorists bear the blame, at least in part, for the rise of Hindu nationalism in India. In eschewing “Enlightenment Secular Humanism”, Nanda argues, these theorists have opened epistemic space for right wing ideologues to justify reactionary politics. Furthermore, she argues that the ideas of postcolonial theory have their roots in the “neo-Hindu revivalist strains of anti-colonial nationalism.”, who she identifies with “Gandhi, Vivekananda, Aurobindo, and even Tagore”. These thinkers were apparently seeking an escape from the idea of modernity present in the “legacy of the British Raj”. This, apparently against the “enlightenment thinkers” of India in which she presents a bizarre counter grouping of “Ambedkar, Periyar, Nehru, M.N. Roy, and Narendra Dabholkar”. This opposition that Nanda sets up is so ludicrous to someone who has even spent a minimal amount of time studying our freedom struggle or any of these thinkers that it requires little comment.
Continue reading The Struggle for a ‘Coloured Modernity’: Meghna Chandra and Archishman RajuThe hopeless quest for a pure incorruptible knowledge – decoloniality and its discontents
[This post by Nivedita Menon is the fourth essay of the series in Kafila titled Decolonial Imaginations. Links to the previous essays are given at the end.
The terms ‘decolonization’ or ‘decolonial’ have become quite critical now, given that the impulse of justice lies at the core of these concepts. Neither postcolonial nor decolonial perspectives are compatible with right-wing ideologies but the fact that Hindutva ideologues in India and the rightwing globally are now trying to appropriate that language makes it seem to some that the very idea of the postcolonial or decolonial is suspect. We believe that this demonizing of decolonial theory from a position defensive of the European Enlightenment needs to be unpacked in the interests of a mutually productive debate. Kafila will be publishing a series of interventions on what the idea of the decolonial imagination involves, locating decolonial theory as speaking from the margins, drawing attention to identities which the orthodox Left subsumed under ‘class’ and which the rightwing in India seeks to assimilate into Brahminism. Additionally the orthodox left’s rejection of spiritual beliefs and inability to engage with them is also a factor that may have produced the space for right wing appropriations of a field marked “religion”.
We hope that these interventions will clear the ground for productive conversations on the left rather than polarised and accusatory claims.]
Introduction
As Hindutva ideologues and the rightwing globally, appropriate the idea of “decolonising”, it seems to many opposed to these trends, that scholarship around decoloniality is itself the problem. Such arguments tie in with earlier ongoing attacks on postcolonial scholarship since the 1990s that virtually accuse it of directly contributing to the rise of the right. Decolonial scholarship is relatively a new arrival in the Anglophone world (since the 2000s), and ever since the rightwing started using that language, the same charges are laid at its door as well. Indeed, the implication (and sometimes outright allegation) is that decolonial/postcolonial scholars were secretly rightwing all along.
This charge I will address in a somewhat different way in the first section, by way of analogies with other bodies of knowledge.
The second section will address another related critique of decolonial thought, that it is “merely epistemic” and does not consider the materiality of structures of power
Finally we will ask the question – when Hindutva claims to be “decolonising”, what is it doing exactly? Continue reading The hopeless quest for a pure incorruptible knowledge – decoloniality and its discontents
Whose Forest is it Anyway? The Forest Rights Act (FRA) and its unintended consequences: Sandeep Menon
Guest post by SANDEEP MENON
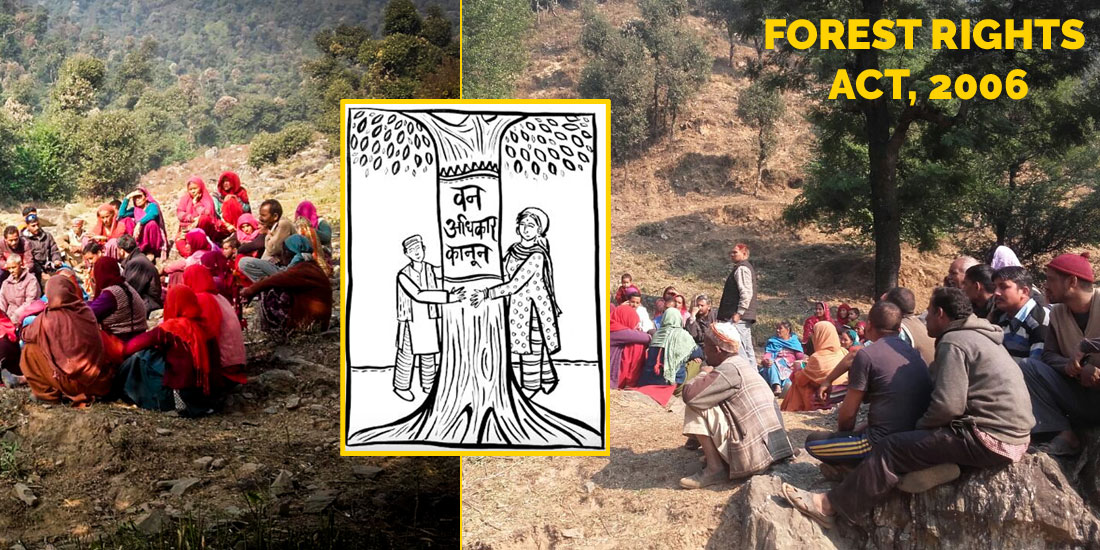

The road to hell is paved with good intentions. That’s the first, visceral reaction that many passionate wildlife conservationists have, when you utter the 3 letters: FRA. The Forest Rights Act (2006) aims to give native tribal and forest dwelling populations ownership of, and decision-making rights over what happens in the wildlife areas that they are residents of. But many conservationists see it as a gateway for rampant encroachment into protected areas.
I was initially a bit more circumspect, having been a longtime advocate for community-based conservation. Having always believed that ivory tower conservation can never work, without putting the people involved at the center of it. But I have also had to temper my position over time, as I witnessed the complexities of how it was playing out on the ground. (ref- https://india.mongabay.com/2020/07/commentary-making-communities-central-to-conservation/ )
Continue reading Whose Forest is it Anyway? The Forest Rights Act (FRA) and its unintended consequences: Sandeep MenonAnti-colonial Thought and the Global Right – An untenable alliance: Ishan Fouzdar
Guest Post by ISHAN FOUZDAR
[This post is the third essay of the series in Kafila titled Decolonial Imaginations. Links to the previous essays are given at the end.
The terms ‘decolonization’ or ‘decolonial’ have become quite critical now, given that the impulse of justice lies at the core of these concepts. Neither postcolonial nor decolonial perspectives are compatible with right-wing ideologies but the fact that Hindutva ideologues in India and the rightwing globally are now trying to appropriate that language makes it seem to some that the very idea of the postcolonial or decolonial is suspect. We believe that this demonizing of decolonial theory from a position defensive of the European Enlightenment needs to be unpacked in the interests of a mutually productive debate. Kafila will be publishing a series of interventions on what the idea of the decolonial imagination involves, locating decolonial theory as speaking from the margins, drawing attention to identities which the orthodox Left subsumed under ‘class’ and which the rightwing in India seeks to assimilate into Brahminism. Additionally the orthodox left’s rejection of spiritual beliefs and inability to engage with them is also a factor that may have produced the space for right wing appropriations of a field marked “religion”.
We hope that these interventions will clear the ground for productive conversations on the left rather than polarised and accusatory claims.]
Introduction
Anti-colonial thought is under attack. Some scholars have accused decolonial and postcolonial theories of nativism. Interestingly, the phenomenon that provoked this accusation is stranger than the accusation itself. The global North and the global South have witnessed an unlikely alliance of anti-colonial rhetoric and right-wing discourse. While the Hindu Right in India deems Muslims to be colonial invaders, the Right Wing in Europe constructs the influx of refugees as a colonial invasion, which will lead to a ‘great replacement’ of White Europeans by West Asian and African refugees. The solution – ‘decolonise’ by expelling the colonisers and reviving the ‘glorious’ ‘indigenous’ past. This invokes several questions: How do European right-wing groups lay claims on decolonisation? Are there common links between these right-wing ‘decolonisation’ projects? More importantly, does the presence of anti-colonial language in right-wing discourse automatically translate to the conclusion that postcolonial and decolonial theories are inherently nativist?
I undertake two broad tasks. First, I lay forth the ‘anti-colonial’ rhetoric of these right-wing projects. Secondly, I condense their similarities and use them to show why anti-colonial thought should not be seen to be irredeemably polluted by this misappropriation.
Before I trace the right-wing appropriation of anti-colonial language, a caveat about the usage of the terms anti-colonial, postcolonial and decolonial is in order. I use anti-colonial thought to broadly bundle postcolonial and decolonial theories. The reason being that both theoretical schools present varying critiques of the socio-cultural and intellectual legacies of colonialism. The difference in the kind of critique separates postcolonialism from decolonial theory. Continue reading Anti-colonial Thought and the Global Right – An untenable alliance: Ishan Fouzdar
Rightwing-Rightwing ‘Bhai Bhai : Who Fears Javed Akhtar?
A ‘unity of purpose’ has been witnessed between Hindu and Muslim supremacists, who consider themselves the sole spokespersons of ‘their community’.
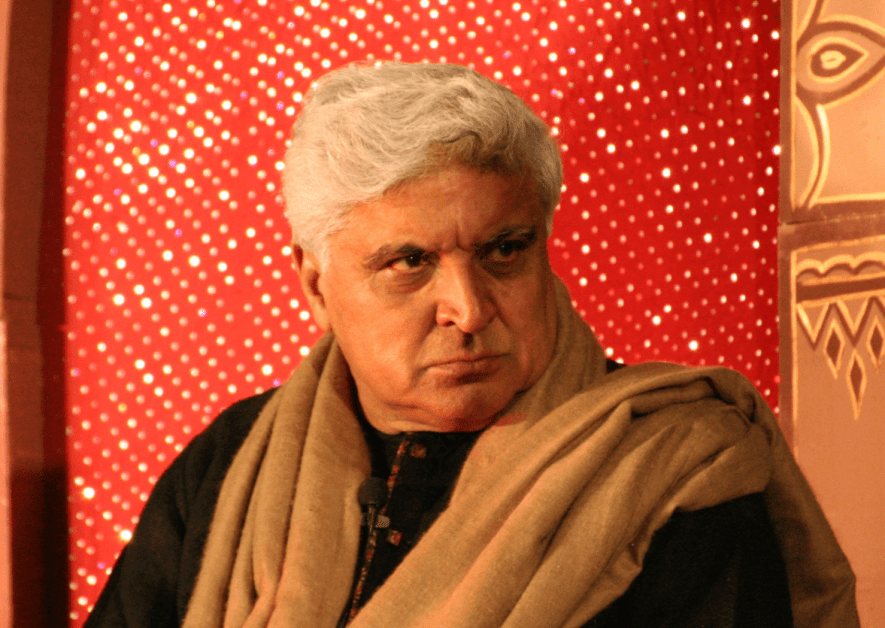

There are rare occasions when literary academies associated with governments wilt under mob pressure.
Rarer are occasions when they even cancel the very programme they had organised with much fanfare.
It has been more than 10 days that West Bengal witnessed such a spectacle, when the West Bengal Urdu Academy suddenly postponed a programme where it intended to discuss ‘Urdu in Indian Cinema’ for four consecutive. Javed Akhtar — one of the foremost living Urdu poets — was also invited as a key speaker in the programme.
Two prominent Islamist organisations in Kolkata, Jamiat Ulema-e-Hind and the Wahyahin Foundation, had protested the invitation, as they considered Akhtar’s views on religion problematic, labelling him as someone who “speaks against religion and God”.
Akhtar is a declared atheist and openly talks about it on public fora, and that had irked these people.
The organisations even threatened to launch a state wide agitation — much on the lines of their agitation against Bangladeshi author Taslima Nasreen which as everyone knows had forced her to leave the state (2007) — if the government did not heed their demand.
Mamata Banerjee, the West Bengal Chief Minister, did not want to take any risk as elections to the state Assembly are not too far.
( Read the full article here : https://www.newsclick.in/rightwing-rightwing-bhai-bhai-who-fears-javed-akhtar)
Beyond Philosophical Gaslighting – Seven theses on Decolonization/ Decoloniality
[This post by Aditya Nigam is the second essay of the series in Kafila, titled Decolonial Imaginations. The first essay can be read here.
The terms ‘decolonization’ or ‘decolonial’ have become quite critical now, given that the impulse of justice lies at the core of these concepts. Neither postcolonial nor decolonial perspectives are compatible with right-wing ideologies but the fact that Hindutva ideologues in India and the rightwing globally are now trying to appropriate that language makes it seem to some that the very idea of the postcolonial or decolonial is suspect. We believe that this demonizing of decolonial theory from a position defensive of the European Enlightenment needs to be unpacked in the interests of a mutually productive debate. Kafila will be publishing a series of interventions on what the idea of the decolonial imagination involves, locating decolonial theory as speaking from the margins, drawing attention to identities which the orthodox Left subsumed under ‘class’ and which the rightwing in India seeks to assimilate into Brahminism. Additionally the orthodox left’s rejection of spiritual beliefs and inability to engage with them is also a factor that may have produced the space for right wing appropriations of a field marked “religion”.
We hope that these interventions will clear the ground for productive conversations on the left rather than polarised and accusatory claims.]
The question of decolonization/ decoloniality keeps surfacing periodically in ill-informed writings and tracts. The target may be postcolonial studies or more recently, decolonial theory, but the attack is always launched in the name of “the Enlightenment” (notice the definite article). The idea behind making what was the European Enlightenment into “the Enlightenment” for the whole world is to claim – as has been done for a couple of centuries since – that the world was lying in “darkness” and “superstition” before the dazzling light of the Enlightenment rescued the inhabitants of the different continents. What were Latin Christendom’s (Europe) “dark middle ages” became the convenient and imagined dark ages of all societies in the world.
Continue reading Beyond Philosophical Gaslighting – Seven theses on Decolonization/ DecolonialityRSS Centenary: In Search of an Icon!
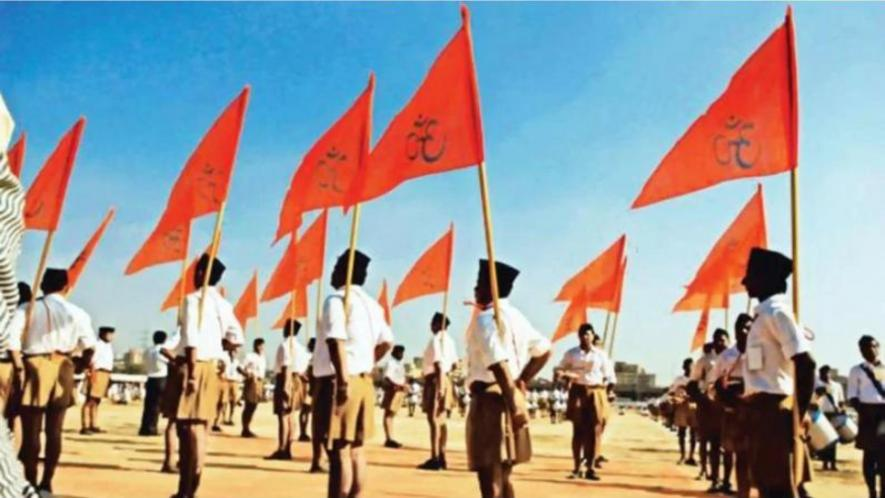

[Centenary celebrations of RSS – the biggest ‘self-proclaimed’ cultural organisation in the world — comprising of Hindus are on.
Much is being said about its longevity etc., and much will be said about it in coming days, it remains to be seen if it is ready to take a fresh look at some discomforting aspects of its own history when it is embarking on a journey towards what it calls as ‘new horizons’]
Ram Lila, the dramatic folk re-enactment of the life of Rama is still popular in Northern India.
Anyone who has watched this programme — especially in villages or towns — might have noticed a particular scene where god curses a sage for his misdemeanour that he will get a donkey’s face for his actions and will not even realise that he has got this new face.
One is reminded of this story — which tells us the great hiatus between claims and reality — whenever an individual or a formation starts bragging about its achievements that have no basis in reality.
Leaders of the Hindutva Supremacist movement in this part of South Asia look no different when they declare from the rooftops the “great role their political ancestors have played during the freedom movement”. It is a different matter that any objective student of India’s history — especially of the Independence struggle — is conversant with hundreds or thousands of pages, books, monographs written or documented to underline the contrary, their meek behaviour and compromising role during the very struggle. [https://www.newsclick.in/rss-centenary-search-icon]
Punjab: Why Proposed ‘Law Against Blasphemy’ Needs to be Discarded
The CCG’s concern that the proposed PPOHS Act is ‘unconstitutional’ and is an ‘open invitation to ‘oppressive misuse’ needs to be heeded.
Image : Courtesy Fiickr
Whether history will repeat itself, that is the question being asked about Punjab government’s renewed attempt to enact a law supposedly against ‘sacrilege’?
Anyone who is a keen observer of the social-political developments in the state knows very well that it has a history of such efforts (2015 and 2018) where similar attempts were made to amend laws related to sacrilege, and both attempts proved unsuccessful as they failed on the yardstick of constitutionality.
As per reports, the proposed Punjab Prevention of Offences against Holy Scriptures Bill, 2025 (PPOHS Act), which was recently referred by the state legislature to a committee for further discussion, has come under the scanner of experts of the Constitution and concerned citizens.
A leading voice among them, namely the Constitutional Conduct Group (CCG) — a platform of retired civil servants and diplomats– has in an open communication underlined how Punjab government’s proposed ‘PPOHS Act’ is ‘unconstitutional’ and is an ‘open invitation to oppressive misuse’ .
[ Read the full article here : https://www.newsclick.in/punjab-why-proposed-law-against-blasphemy-needs-be-discarded]
Sleeping With the Enemy? Postcolonialism, Misread and Misjudged: Shamayita Sen
Guest post by SHAMAYITA SEN
[This post is the first of a series in Kafila, titled Decolonial Imaginations.
The terms ‘decolonization’ or ‘decolonial’ have become quite critical now, given that the impulse of justice lies at the core of these concepts. Neither postcolonial nor decolonial perspectives are compatible with right-wing ideologies but the fact that Hindutva ideologues in India and the rightwing globally are now trying to appropriate that language makes it seem to some that the very idea of the postcolonial or decolonial is suspect. We believe that this demonizing of decolonial theory from a position defensive of the European Enlightenment needs to be unpacked in the interests of a mutually productive debate. Kafila will be publishing a series of interventions on what the idea of the decolonial imagination involves, locating decolonial theory as speaking from the margins, drawing attention to identities which the orthodox Left subsumed under ‘class’ and which the rightwing in India seeks to assimilate into Brahminism. Additionally the orthodox left’s rejection of spiritual beliefs and inability to engage with them is also a factor that may have produced the space for right wing appropriations of a field marked “religion”.
We hope that these interventions will clear the ground for productive conversations on the left rather than polarised and accusatory claims.]
This article comes as a response born from a deep sense of intellectual anguish and frustration. It is a rebuttal to a YouTube video titled The Left’s Accidental Gift to Hindu Nationalism posted by one of India’s leading independent news portals, The Wire on 14th August 2025. The video attempts to summarize Meera Nanda’s critique of Postcolonial Left as elaborated in her latest treatise, Postcolonial Theory and the Making of Hindu Nationalism: The Wages of Unreason (2025). While I have read the newly published work, including the excerpt published in The Wire which have been shared widely in popular social media platforms, this piece restricts itself to the Video which comprehensively outlines Nanda’s arguments. An extensive engagement with the critique that Nanda mounts is reserved for some other time.
Continue reading Sleeping With the Enemy? Postcolonialism, Misread and Misjudged: Shamayita SenTeachers, Straw, and the Combine Harvester – Peasant Household’s Ecological Ledger in Assam: Bonojit Hussain
Guest post by BONOJIT HUSSAIN
I did not come to the village to do research. I came to farm for the market—and to do it without breaking the village’s social and ecological ledger. I returned as a nephew and a neighbour. For six years I have lived inside this world of muddy fields, failed pumps, anxious harvests, and commonsense wisdom passed across haat stalls. Six years on, I am only now seeing a glimmer of hope for a workable path.
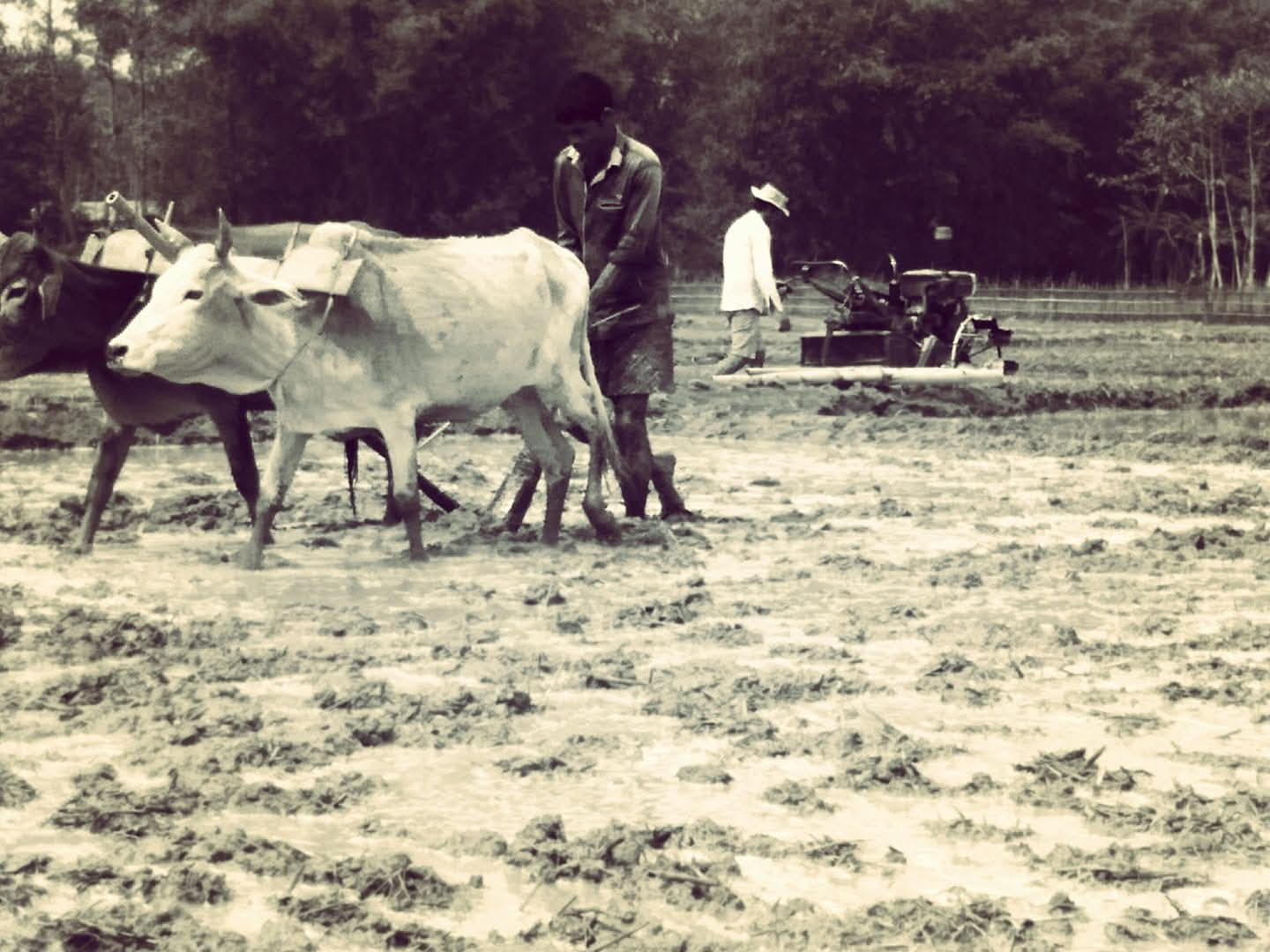

What I write here is not sociology in the professional sense, but a testimony from within the living contradictions. My focus is on the choices and constraints of the khilonjiya peasant household—native, often subsistence-oriented communities whose economic logic is deeply tied to ecological and social reproduction. This is a distinct reality from the highly commercialized production systems found in some other parts of the state.
Continue reading Teachers, Straw, and the Combine Harvester – Peasant Household’s Ecological Ledger in Assam: Bonojit HussainWhen Police Comes Visiting Bookshops!
How saffron forces weaponise ignorance and stigmatise intellectauls

Silence gives consent
[Qui tacet consentire videtur – In Latin]
“Intellectual terrorists” are “more dangerous than cross-border terrorists”
These were the pearls of wisdom of the then Human Resource Development minister, who was addressing a conference of the Bharatiya Janata Yuva Morcha (December 19, 2001). Murli Manohar Joshi had even asked the ‘nationalist youths’ to counter ‘both types of terrorism effectively.’
…It would be 25 years soon since these objectionable remarks were targeted at India’s topmost historians, scholars, public intellectuals, even provoking followers to deal with them effectively’ like the way they deal with ‘cross border terrorists.’
Later commenting on these controversial remarks, the legendary historian Romila Thapar had famously said: ‘And then the government fell. But the books continued!”
Time for Thought Police?
As everybody can see, there is a sea change in the situation since the past more than a decade in this part of South Asia…
…..The target of attacks has now become broader, more expansive and more unpredictable. It is no longer restricted to ‘leftist’ ‘progressive’ writers, historians.
The recent move to ban 25 books on Kashmir history at a single go ‘for propagating false narrative and secessionism‘ — written by a spectrum of national and international scholars — which even do not share a similar world view, books which had been in circulation for years, even decades together is a case in point.
This list of authors includes, A G Noorani, Arundhati Roy, Anuradha Bhasin, Sumanta Bose, Victoria Schofield and several others… [Read the full article here : https://www.newsclick.in/when-police-comes-visiting-bookshops]
A Strategy for India’s Tryst with Its Destiny : Arun Maira
Democracy Dialogues Lecture 41
Organised by New Socialist Initiative
Title: A Strategy for India’s Tryst with Its Destiny
Speaker: Arun Maira, Author, Thinker, Former Member of the Planning Commission of India
Date and Time: August 31, 2025, 6 PM IST
The lectures are also live streamed at facebook.com/newsocialistinitiative.nsi
Abstract:
I will share what I have learned about the process of transforming complex systems, the changes necessary in ideologies, and in the way in which public policies are being made, for India to progress towards its vision of poorna swaraj. The following points indicate an outline of the argument I plan to make in the talk:
• Global governance has broken down. The world is in disorder.
• India is strategically vulnerable. It is a long way off from its ‘tryst with destiny’ of poorna swaraj.
• India must become much more self-reliant, and less dependent on the US and China to protect its strategic autonomy. It must find its own democratic path to strengthen its society and economy. The US (and the West) cannot provide a blueprint.
• Development and progress are processes of learning.
• Nations are complex ‘self-adaptive’ systems.
• Power and wealth in a system accumulate by a process of cumulative causation.
• The process of change must be democratic for new ideas to emerge.
I have explained such ideas in my book, Reimagining India’s Economy: The Road to a More Equitable Society, published this year, and in some previous books.
About the Speaker:
Arun Maira is an eminent author, a strategic thinker and a former member of the Planning Commission of India. He had joined the Commission at the invitation of then Prime Minister Dr Manmohan Singh himself. Mr. Maira has had a distinguished career as an enlightened business leader and management consultant. He worked as Executive Director on the Board of Tata Motors and later as the Chairman of Boston Consulting Group. He has authored many books including Transforming Systems: Why the World Needs an Ethical Toolkit; Transforming Capitalism: Improving the World for Everyone; Redesigning the Aeroplane While Flying: Reforming Institutions; Shaping the Future: A Guide for Systems leaders; and most recently, Reimagining India’s Economy: The Road to a More Equitable Society, published in June 2025.
